- What Are Conditionals and Why Are They Useful in IELTS Writing Task 1?
- Types of Conditionals You Should Know for IELTS Writing Task 1
- How to Use Conditionals to Discuss Possible Trends or Predictions
- Practical Examples of IELTS Conditionals Writing Task 1
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Conditionals
- Tips to Master IELTS Conditionals Writing Task 1
- Combining Conditionals with Grammar and Vocabulary
- Sample Paragraph Using Conditionals in IELTS Writing Task 1
- Final Thoughts
When preparing for IELTS Writing Task 1, you might wonder how to talk about possible trends, future predictions, or hypothetical scenarios effectively. One of the best ways to do this is by using IELTS conditionals writing task 1 correctly. As an IELTS instructor with years of experience, I can tell you that mastering conditionals and hypothetical grammar can add sophistication to your writing and help you explain data more precisely.
In this post, I’ll explain when and how to use different types of conditionals in IELTS Writing Task 1. I’ll provide examples and tips that you can apply directly in your essays. To complement your grammar, don’t forget to visit my detailed guides on IELTS Writing Task 1 Grammar for Band 7–9 and IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary Complete Guide. For official materials, explore the IELTS official website, the British Council, and IDP IELTS.
What Are Conditionals and Why Are They Useful in IELTS Writing Task 1?
Conditionals are sentence structures that express cause-and-effect relationships, possibilities, or hypothetical situations. They are often used in Writing Task 1 to:
- Discuss trends that depend on certain conditions
- Predict future outcomes based on current data
- Explain what might happen if changes occur
Using conditionals correctly shows your grammatical range and allows you to describe data in a more nuanced way — something examiners appreciate for higher band scores.
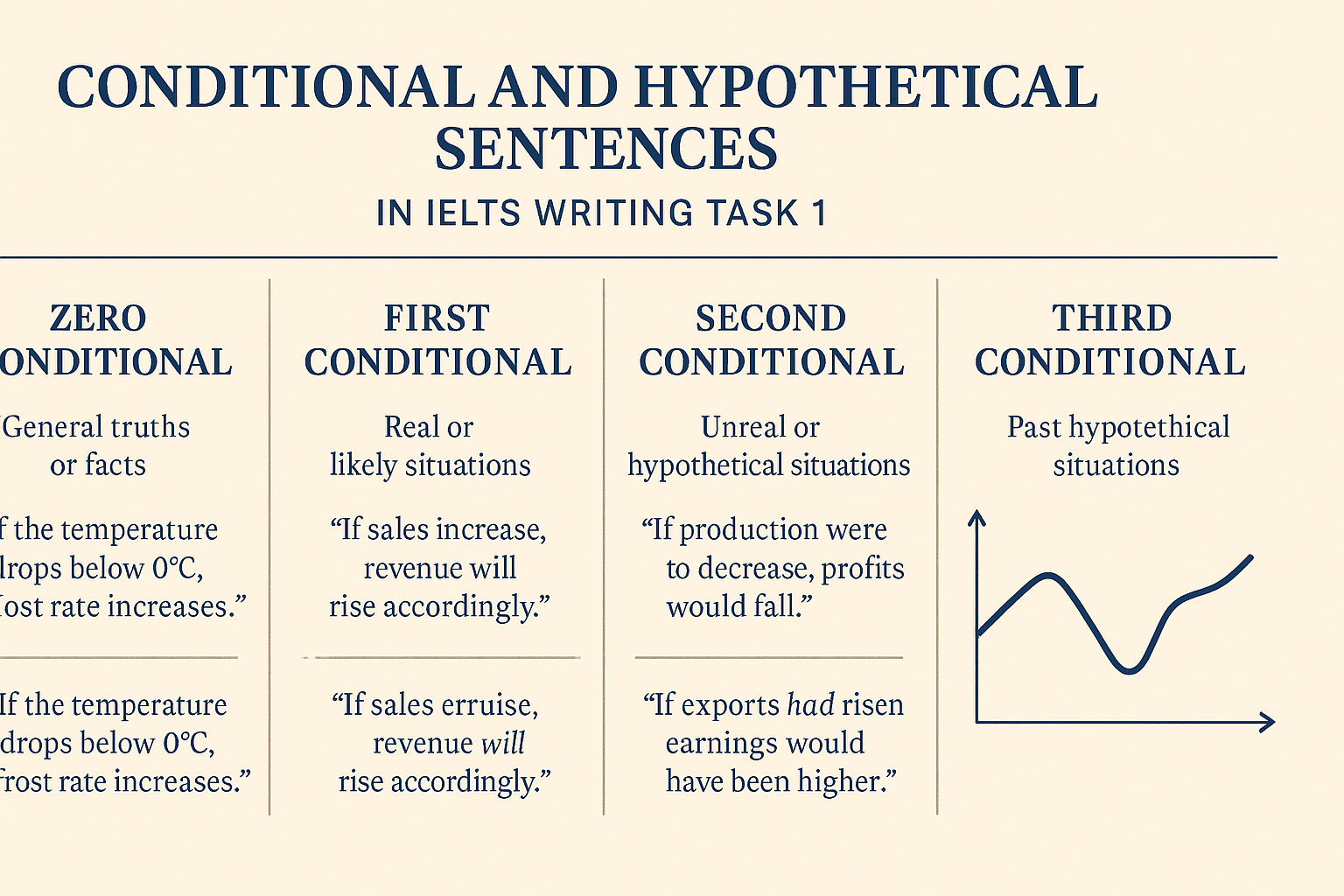
Types of Conditionals You Should Know for IELTS Writing Task 1
There are four main types of conditionals you can use:
1. Zero Conditional: Facts and General Truths
Used for facts or things that are always true if the condition happens.
Structure:
If + present simple, present simple
Example:
If the temperature rises, the ice melts.
In Task 1, this might be less common but useful when describing universal relationships in data.
2. First Conditional: Real Possibilities in the Future
Used to talk about real or likely situations in the future.
Structure:
If + present simple, will + base verb
Example:
If sales continue to increase, profits will grow further.
This is very useful for discussing future projections or trends shown in graphs.
3. Second Conditional: Hypothetical or Unreal Situations
Used for unlikely or hypothetical situations in the present or future.
Structure:
If + past simple, would + base verb
Example:
If the population grew faster, the city would need more housing.
This adds sophistication when discussing hypothetical changes.
4. Third Conditional: Hypothetical Past Situations
Used to talk about things that didn’t happen in the past and their imagined results.
Structure:
If + past perfect, would have + past participle
Example:
If the government had invested more in infrastructure, the economy would have improved.
Though less common in Task 1, it can be used in reports discussing past policies or outcomes.
How to Use Conditionals to Discuss Possible Trends or Predictions
In IELTS Writing Task 1, you often describe data trends and future forecasts. Here’s how to use conditionals effectively:
- Use the first conditional to talk about realistic future changes.
- Use the second conditional for less likely or hypothetical scenarios.
- Use conditionals to explain cause and effect related to trends.
Example:
If the current growth rate continues, the population will double by 2050.
If resources were better managed, the decline in employment might be reversed.
Practical Examples of IELTS Conditionals Writing Task 1
- If energy consumption increases at this rate, renewable sources will become essential.
- If the number of tourists fell last year, revenues would have decreased significantly.
- If the city invested more in public transport, traffic congestion would reduce.
- If temperatures rise beyond 2 degrees, the ice caps will melt faster.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Conditionals
- Mixing tenses incorrectly: Always match the correct tense pair in the conditional.
- Using “will” in the if-clause (incorrect in first conditional).
- Confusing the use of “would” and “will.”
- Overusing conditionals when simple statements suffice.
Tips to Master IELTS Conditionals Writing Task 1
- Practice writing sentences using all four conditionals.
- Read official IELTS Writing Task 1 model answers to see conditionals in context.
- Use conditionals sparingly and appropriately to enhance, not complicate, your writing.
- Review grammar rules regularly, such as in my IELTS Writing Task 1 Grammar for Band 7–9 guide.
Combining Conditionals with Grammar and Vocabulary
Using conditionals correctly will help demonstrate your grammatical range, but remember to also use accurate vocabulary. Pair conditionals with precise verbs and linking phrases for a polished report. For vocabulary tips, visit my IELTS Writing Task 1 Vocabulary Complete Guide.
Sample Paragraph Using Conditionals in IELTS Writing Task 1
If the current trends continue, the urban population will increase by 30% by 2030. If investments were made in green technology, energy consumption could decrease. However, if emissions remain unchecked, environmental damage would worsen.
Final Thoughts
Mastering IELTS conditionals writing task 1 and hypothetical grammar allows you to describe trends, causes, and predictions more effectively. Use conditionals carefully and accurately to add nuance and professionalism to your reports.
For further practice and tips, explore official IELTS resources at the British Council and IDP IELTS, and make sure to study my comprehensive grammar and vocabulary guides linked above.
Good luck with your IELTS preparation!




3 Responses
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
Hello my loved one! I wish to say that this post is amazing, nice written and
come with almost all significant infos. I’d like to see more posts like
this .
I savor, lead to I found exactly what I used to be taking a look for.
You have ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man.
Have a nice day. Bye